Crb 65 Score / Severity And Outcomes According To Crsi Crasi And Crb 65 Groups I Download Scientific Diagram
65 years of age or older. Serum cortisol was measured and its.

Ps Index And Crb 65 Scores In Relation To In Hospital Mortality Of 95 Download Table
CRB-65 removes BUN from the criteria with no difference in predictability.

Crb 65 score. AMBOSS 5 Tage unverbindlich testen. Aim The study sought to validate CRB-65 and assess its clinical value in community and hospital settings. And SIRS 0686 and 0659 0651 0719 and 0623 0693 respectively.
Laborwerte welche für den Score beurteilt werden. A CRB-65 score can be calculated by omitting the blood urea nitrogen value which gives it a point range from 0 to 4. Der CRB-65-Index ist ein klinischer Score mit dem der Schweregrad einer ambulant erworbenen Pneumonie abgeschätzt werden kann.
The CRB-65 score may help with making a decision on referring adults. Clinical judgement is essential in disease severity assessment of community acquired pneumonia CAP. Both the CURB and CRB-65 scores can be used in the hospital and out-patients setting to assess pneumonia severity and the risk of death.
CRB-65 can be used as useful screening tools to. The CURB-65 calculator can be used in the emergency department setting to risk stratify a patients community acquired pneumonia. Scores of 2 require more assistance and might need hospital admission and also the risk grows exponentially.
CRB - 65 0816 and 0735 0786 0843 and 00702 0766. Both predict death in a class 3 pattern with mortality rates of approximately 13 PSI class IIII CRB. Der CRB-65-Index ist ein klinischer Score mit dem der Schweregrad einer ambulant erworbenen Pneumonie abgeschätzt werden kann.
A modified version of the score known as CRB-65 is often performed in general practice to assess the need for hospital admission. Die einzelnen Buchstaben stehen für die englisch bezeichneten klinischen Befunde bzw. Each of the 5 parameters in CURB-65 is awarded 1 point for a maximum of 5 total points.
In the case of cumulative scores of 0 or 1 outpatient treatment is advisable as the mortality risk is less than 3 in 30 days. QSOFA 0779 and 0724 03747 0808 and 0690 0755. The CURB-65 Score includes points for confusion and blood urea nitrogen which in the acutely ill elderly patient could be due to a variety of factors.
AUROC values 95 CI for predicting ICU admission and in-hospital mortality were as follows. Thus if the patient needed supplemental oxygen when transported by ambulance before arrival at the ED the SpO 2 measured by the crew was used if it was lower than the SpO 2 recorded on arrival at the. Given that the CRB-65 is easier to handle we favour the use of CRB-65 where blood urea nitrogen is unavailable.
CRB-65 score of 3 or more urgent admission to hospital is. An earlier more detailed score known as the Pneumonia Severity Index also known as the PORT score has also been prospectively validated. Treatments depend on the score and there are usually local hospital guidelines to follow.
The CURB-65 score was derived and validated based on 1068 patients from three prospective studies in the UK New Zealand and the Netherlands. The CRB-65 score was calculated according to the ori-ginal publication9 The lowest SpO 2 recorded either by the ambulance crew or at the ED was used when the DS CRB-65 score was calculated. Background The CRB-65 score is a clinical prediction rule that grades the severity of community-acquired pneumonia in terms of 30-day mortality.
In den kommenden Wochen veröffentlichen wir sukzessive weitere medizinische Rechner und Scores für den klinischen Einsatz. CRB-65 c onfusion r espiratory rate b lood pressure age 65 years CRB-65 Feedback Einfach zu erhebender 4 klinische Parameter umfassender Score der zur Beurteilung des Letalitätsrisikos bei ambulant erworbener Pneumonie CAP community acquired pneumonia entwickelt wurde. Availability of the CRB-65 score 90 was far superior to that of CURB 65 due to missing blood urea nitrogen values P 0001.
Design of study Systematic review and meta-analysis of validation studies of CRB-65. CRB 0774 and 0707 0742 0803 and 0673 0739. 65 years of age or older patients who have a CRB65 score of 0 are at low risk of death and do not normally require hospitalisation for clinical reasons patients who have a CRB65 score of 1 or 2 are at increased risk of death particularly with a score of 2 and hospital referral and.
This ensures that treatment is based on the severity of. Weiterführende Inhalte zum Thema Pneumonie in AMBOSS. Hans-Joachim Kabitz Konstanz hin.
Outpatient management is best for the patient. The pneumonia severity index PSI1 and the CURB score and its modifications CURB-65 CRB-6525 In the meantime it has become evident that the PSI and the CRB-65 score as the most simple modification of the original CURB score perform equivalent in terms of prediction of inhospital death. Two lines of investigation have resulted in two competing tools of severity assessment.
Zur Beurteilung klinischer Fragestellungen müssen regelmäßig spezifische Werte ermittelt werden. The CRB-65-score is a clinical score that is used to roughly estimate the severity of community-acquired pneumonias. CURB-65 ist ein Akronym für ein klinisches Beurteilungssystem für Patienten mit Lungenentzündung Pneumonie.
Aureus Moraxella catarrhalis Enterobacterales Mycoplasma pneumoniae Legionella spp Chlamydophila pneumoniae Consider SARS-CoV-2 and influenza during epidemic season. Mithilfe des CRB-65-Scores alternativ CURB-65-Score kann der Schweregrad der Erkrankung abgeschätzt und damit die Indikation für eine stationäre Aufnahme einfacher gestellt werden. CRB-65 is a modified version of the CURB-65 tool for assessing severity of community-acquired pneumonia and determining whether the patient requires inpatient or outpatient treatment.
Assessing mortality risk using the CRB65 score in primary care informs clinical judgement and supports decisionmaking about whether care can be managed in the community or if hospital assessment is needed. CURB-65 Score for Pneumonia Severity. The score can also be used to predict 30-day mortality.
Weiterführende Inhalte zum Thema Pneumonie in AMBOSS. Blood pressure systolic of 90 mmHg or less or diastolic of 60 mmHg or less. Zusätzlich zu den bekannten Parametern neu aufgetretene Verwirrtheit Atemfrequenz 30min Blutdruck 9060 mmHg und Alter 65 kommen nun weitere Punkte hinzu die ein erhöhtes Risiko.
90 mmHg 1 Alder 65 år 1 I almen praksis udelades carbamidmåling CRB-65. The overall CURB-65 score therefore ranges between 0 meaning no risk pneumonia if diagnosed and 5 which is indicative of very severe pneumonia. The CURB-65 score estimates mortality of community-acquired pneumonia to help us determine whether inpatient vs.
CRB-65-Score ist auch im hausärztlichen Bereich hoch relevant für die Einschätzung des Schweregrads einer ambulant erworbenen Pneumonie. Der Wert gibt eine statistische Wahrscheinlichkeit an an der Pneumonie zu versterben. This omits ht urea measurement.
The score corresponds to the statistical probability. Patienter med CRB-score i intervallet 2-4 bør indlægges. Moderate - based on clinical judgement and guided by CRB-65 score 1 or 2 or CURB-65 2 or PSI score III Usual Pathogens.
Damit diese Werte jederzeit schnell zur Hand sind stellen wir hier erste Rechner und. And 65 years old or older. A comparison between the two scoring systems demonstrated a slightly better performance using the PORT score as compared to the CURB-65 score.
The score is determined by awarding one point for each of the following features. 1 Blodtryk diastolisk 60 mmHg eller systolisk. Both the CURB and CRB-65 scores can be used in the hospital and out-patients setting to assess pneumonia severity and the risk of death.
Respiratory rate of 30 breathsmin or greater. CURB-65 score Point Confusion 1 Uræmi carbamid 7 mmoll 1 Respirationsfrekvens 30min.

The Use Of The Crb 65 Severity Of Illness Score To Determine The Need For Admission Of Patients With Community Acquired Pneumonia Presenting To An Emergency Department Semantic Scholar
Determining Need For Hospitalisation Evaluation Of The Utility Of The Crb 65 Score In Patients With Community Acquired Pneumonia Presenting To An Emergency Department Kabundji South African Medical Journal

Modifications Of The Curb65 And Crb65 Scores For Prediction Of 30 Day Download Table

Validation Of The Qsofa Score Compared To The Crb 65 Score For Risk Prediction In Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Systolic Blood Pressure Below 90mmhg And Assessment Of Covid 19 Severity With Crb 65 Score The New Neander S Medical

The Use Of The Crb 65 Severity Of Illness Score To Determine The Need For Admission Of Patients With Community Acquired Pneumonia Presenting To An Emergency Department Semantic Scholar

Outpatient Vs Inpatient Treatment Of Community Acquired Pneumonia Fpm

Validity Of British Thoracic Society Guidance The Crb 65 Rule For Predicting The Severity Of Pneumonia In General Practice Systematic Review And Meta Analysis British Journal Of General Practice

Management Of Community Acquired Pneumonia An Observational Study In Por

Continuous Variables Of Curb65 And Crb65 Scores With The Following Download Scientific Diagram

Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Decision Support Training Primary Care Setting Agency For Healthcare Research And Quality
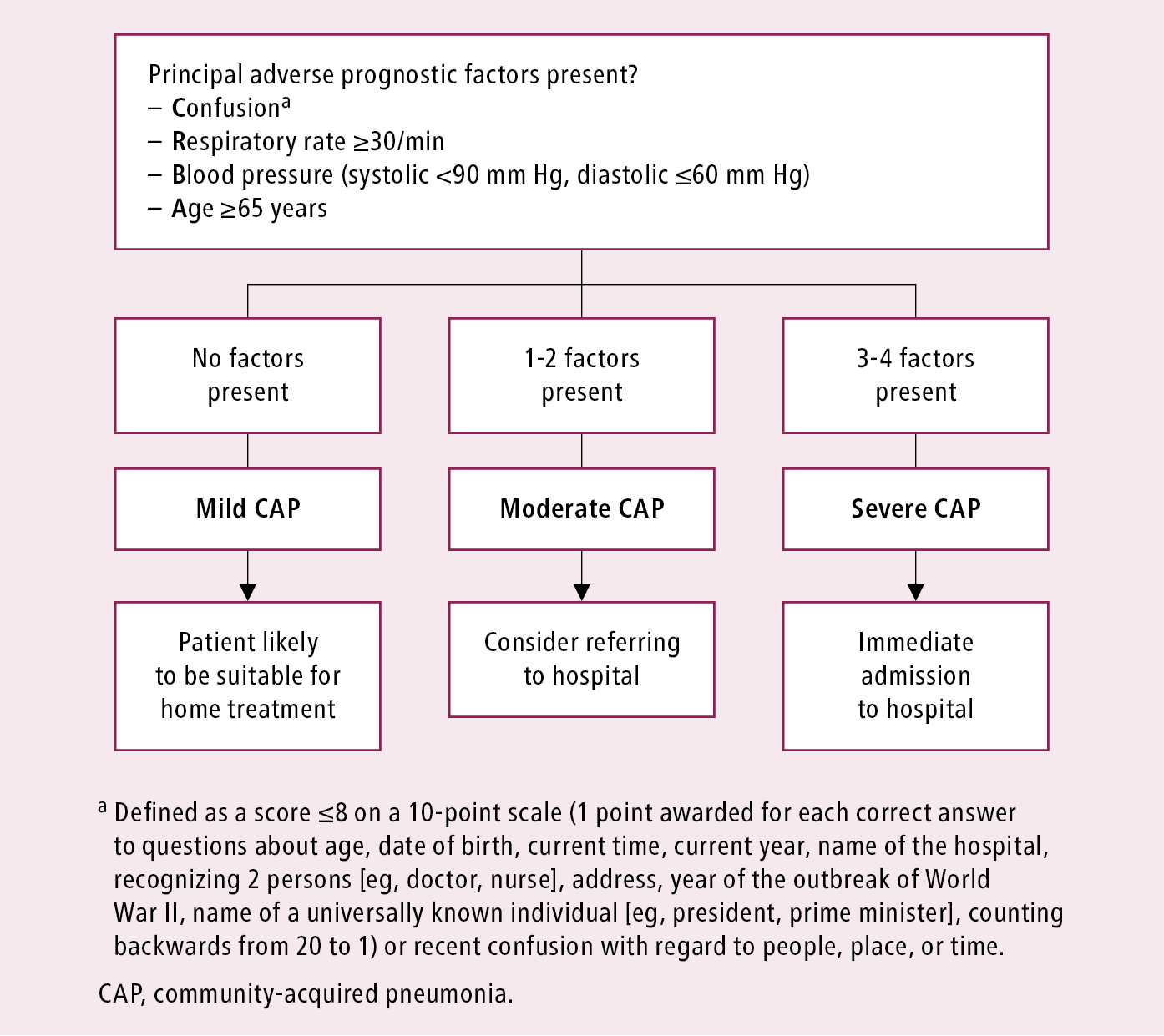
Figure 031 1 6787 Severity Assessment Of Community Acquired Pneumonia In The Outpatient Setting Crb 65 Score Adapted From The 2009 British Thoracic Society Guidelines Mcmaster Textbook Of Internal Medicine

Validity Of British Thoracic Society Guidance The Crb 65 Rule For Predicting The Severity Of Pneumonia In General Practice Systematic Review And Meta Analysis British Journal Of General Practice

Severity And Outcomes According To Crsi Crasi And Crb 65 Groups I Download Scientific Diagram

Defining Community Acquired Pneumonia Severity On Presentation To Hospital An International Derivation And Validation Study Thorax

Validity Of British Thoracic Society Guidance The Crb65

Platelet Counts In Relation To Crb 65 And Ps Index Scores Of 95 Cap Download Table

Community Acquired Pneumonia Non Covid 19 Management Recommendations Bmj Best Practice
